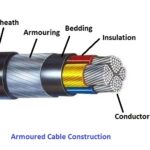
Armoured cables represent a significant advancement in the field of electrical engineering, designed to offer enhanced safety and protection in demanding industries and environments. Comprising various elements such as conductors, insulation, bedding, armour, and sheath, these power transmission linchpins are constructed with careful attention to detail to ensure optimal resilience and reliability. Understanding the anatomy of these cables, the process of their construction, the diverse types, their applications across various sectors, and the pertinent maintenance and safety protocols can provide anyone with a comprehensive insight into the world of armoured cables.
Construction of Armoured Cables
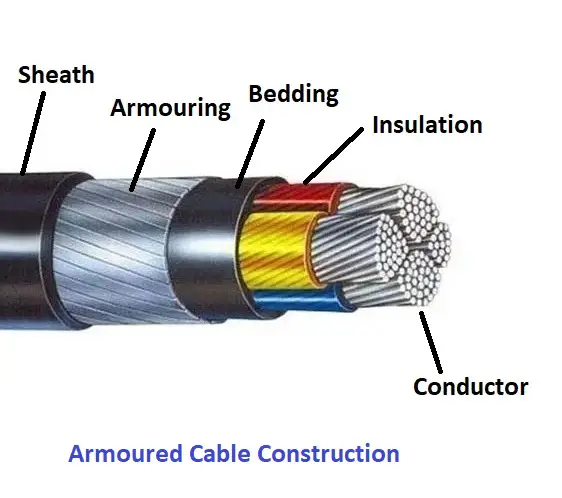
Conductors
Conductors are essentially the heart of any cable, including armoured ones. These are typically made up of materials with high electrical conductivity, such as copper or aluminium. Conductors form the path for the electrical current to flow between the power source and the device.
Insulation
Insulation is the protective layer enveloping the conductors. The role of insulation is two-fold. First, it prevents the current from escaping the conductor, thereby, maintaining the efficiency of power transmission. Second, they protect the user from direct contact with the conductors, preventing potential electric shocks. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), and ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) are common materials used for insulation.
Bedding
The bedding, sometimes also known as the filler, is another key part of an armoured cable. Positioned over the insulation layers, the bedding material serves several phenomenal roles. They equalize the pressure exerted equally across the cable when the armour layer is added. They maintain the roundness of the cable so that the armour fits perfectly. More crucially, the bedding provides a clean, smooth base for the armour to sit on, minimizing potential damage.
Armour
Armour, the attribute that grants the armoured cable its name, is the mechanical protection layer added over the bedding. The armour helps in protecting the cable from external physical stresses, which can range from routine wear-and-tear, and rodent attacks, to extreme conditions such as direct underground burial or underwater installations. The type of armour used can vary depending upon the specific application and can include steel wire, steel tape, or aluminium.
Outer Layer: The Sheath
The sheath, also commonly referred to as the jacket, serves as the outer cover of an armoured cable. This protective shell does a crucial job – it shields the underlying elements of the cable from a range of damaging environmental factors. These include but aren’t limited to, moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation. A sheath that is chosen well can significantly enhance the longevity and durability of a cable. The materials used for the sheath are typically chosen based on where and how the cable will be used. Some of the frequently chosen materials for this purpose are PVC, low smoke zero halogen (LSZH), and neoprene.
Types of Armoured Cable
Steel Wire Armoured Cable (SWA)
Steel wire armoured cable, abbreviation is SWA, is one of the most common types of armoured cables used in electrical power distribution. It features a strong steel wire conductor that is assembled with a layer of insulation. The steel wire armour provides excellent tensile and compressive strength, enhancing the cable’s mechanical protection capabilities. SWA cables are widely used in underground and cable ducts electrical installations, particularly in 11 kV and 33 kV applications.
Steel Tape Armoured Cable (STA)
Steel tape armoured cable (STA) is another type of armoured cable that uses a layer of steel tape for mechanical protection. The steel tape armour provides high permeability and excellent magnetic shielding effect, making it suitable for protecting fibre optic cables. STA cables are often used in applications where low-frequency interference needs to be minimized.
Aluminium Wire Armour Cable (AWA)
Aluminium wire armoured cables, also called as AWA cables, are designed to provide mechanical stress protection. These cables are suitable for direct burial and outdoor or underground installations.
Unlike steel armour, which can induce eddy currents and cause overheating in AC distribution, the non-magnetic aluminium reinforcement in AWA cables prevents such problems. AWA cables are found in applications where magnetic fields need to be minimized.
Braid Wire Armour
Braided armour cables feature a tightly meshed tubular structure formed by interwoven fine copper wires. This braided structure wraps around the conductor, providing mechanical protection and suppressing magnetic fields. The suppression of magnetic fields reduces electromagnetic interference between cables and nearby equipment, making braided armour cables suitable for high-speed signal transmission in environments prone to mechanical damage.
Applications of Armoured Cables
Safety and Protection of Armoured Cables
Armoured cables stand out in terms of safety and protection. Due to their robust construction, these cables can endure extreme conditions that often correlate with heavy-duty applications. The metal armour provides a formidable barrier against severe mechanical stress, such as impact and crushing forces. Furthermore, the armour helps shield the insulation from chemical degradation and temperature extremes, ensuring the integrity of the electrical conductors.
Additionally, the armour provides a measure of grounding safety. If the cable is damaged and a hot wire touches the armour, the grounded armour will trigger a breaker to interrupt the circuit, thereby providing an additional layer of safety.
Application of Armoured Cables across Various Industries
The protective and resilient nature of armoured cables makes them highly demanded in a wide range of applications and industries. In construction and infrastructure development, these cables are used for power transmission in both underground and overhead installations. Their toughness and ability to withstand harsh environments also make them suitable for use in the utilities and renewable energy sector, such as for power links in wind turbines and solar panels.
In the mining and marine industries, where environment conditions can be severe and unpredictable, the use of armoured cables is prevalent due to their strength and endurance. Furthermore, these cables are also used in heavy industries and manufacturing, where machinery and equipment require reliable and continuous power supply.
To sum it up, armoured cables are virtually a non-negotiable necessity in industries that operate within harsh environments. These cables provide a robust, secure method for the transmission of power and data in various circumstances.
Understanding the Uses of Armoured Cable
Armoured cable, primarily used in power distribution, is a versatile solution for various industrial applications due to its protective properties. It’s the go-to choice in environments that demand a high level of mechanical protection and electrical safety like commercial buildings, hospitals, and industrial plants. Moreover, armoured cables are often found in heavy-duty motors, HVAC systems, and street lighting, as well as subterranean placements, thanks to their resilience against physical damage and harsh external conditions.
Safety Measures in Installing and Handling Armoured Cables
Handling and installing armoured cables demand a level of caution to uphold safety. Prior to installation, ensure the cable is suitable for its intended use, taking into account factors such as the environment, the nature of the application, and the cable’s rated temperature and voltage.
During installation, avoid twisting or bending the cable beyond its minimum bending radius. Excessive bending can damage the armour and compromise its effectiveness.
Remember that the ends of the metallic armour can be sharp. Handle with care to prevent injuries. Use of appropriate protective gear, such as gloves, can be highly beneficial in this regard.
A routine visual inspection can also help spot potential issues early. Always check for signs of damage or exposed wires before working with armoured cables. Damaged cables should be repaired or replaced immediately.