A fuse is a small wire connected between two terminals that are mounted on an Insulating base and connected in series with a circuit. A fuse is the simplest and cheapest current interrupting device used to protect equipment from overload or short circuit faults in medium and low voltage applications. A high rupturing capacity fuse is a full form of HRC fuse. It is reliable and accurate protection for motor and other distribution networks.
Table of Contents
What is HRC fuse
Definition: HRC fuse is an abbreviation of a high rupturing capacity cartridge fuse. In high rupturing capacity fuse, the fuse link carries a short circuit current up to a certain limit. If the limit exceeds the link blows off and it disconnects the faulty circuit.
It has the advantage over normal rewirable fuse as it has high accuracy and reliable operation.
HRC fuse is normally used to protect distribution systems and electrical motors. The HRC fuse diagram is shown below.

Construction of HRC Fuse
HRC fuse construction is done using the cylindrical body of ceramic material. The fuse element is fitted inside the body and surrounding area filled with pure powdered quartz.
The two ends of the fuse element are connected to the metal end caps which are screwed to the ceramic body to withstand the pressure developed under short circuit conditions. The contact blade is welded to metal end caps.
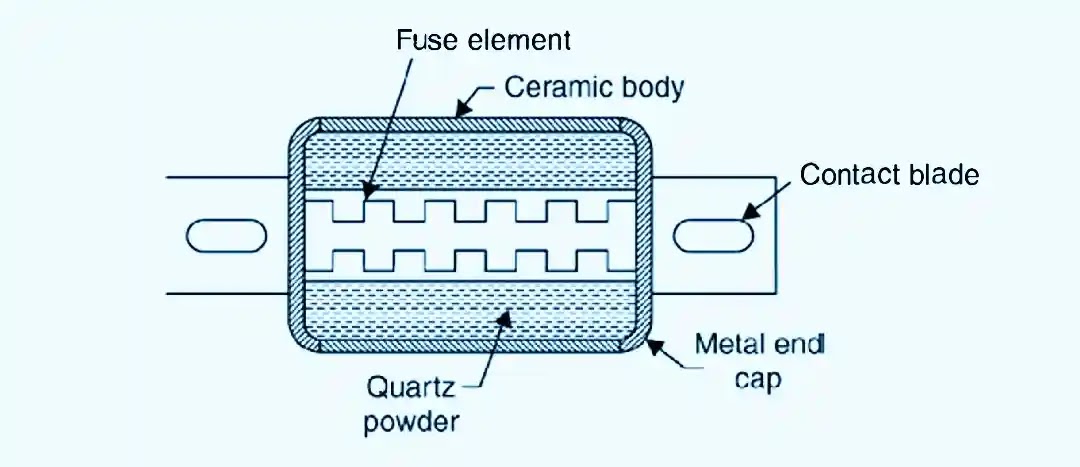
The fuse element is made of either pure silver or bimetallic material. The fuse element is generally constructed with two or more sections of the joint which are joined by means of a tin joint.
The long cylindrical wire is not used for fuse elements because after a short circuit, it will melt and will form a string of droplets and an arc will form between each droplet. Later on, these droplets will also evaporate and a long arc will be struck between droplets.
Due to this tin is used between joints, the purpose of the tin joint is to prevent the formation of long arc during short circuit conditions as the melting point of tin metal is low i.e 230 degrees as compared to silver fuse element 960 degrees. Hence tin melts first under fault conditions and prevents the silver link from attaining a high temperature.
Working Principle Of HRC Fuse
Under normal working conditions, the HRC fuse link carries a normal rated current, the heat energy developed is not sufficient to melt the fuse element.
But under short circuit conditions or when the fault occurs, a high fault current starts flowing through the fuse link and it melts before the fault current reaches its first peak.
As the element melts it vaporizes and scatters, as an arc forms the chemical reaction between element vapor and quartz powder, forming a high resistance substance that helps in quenching the arc thus fault current interrupts.
Types of HRC Fuse
- NH Type
- DIN Type HRC Fuse
- Blade Type
NH Type
NH Type HRC fuse is mostly used for low and medium voltage applications. this type of fuse provides protection against overload and short circuits.
This type of fuse protects the motor against overload and short circuit conditions.
DIN Type HRC Fuse
DIN-type HRC fuses are available in a wide range of current capacities.
DIN fuses are used based on characteristics and temperature conditions for different purposes. This type of fuse is available in numerous voltage levels and can be even used for transformer protection.
Application of DIN fuses is in gas-covered switchgear and transformer.
Blade Type
Blade-type fuses are also called Plug I-type fuses. these fuses are available with a plastic body and two metal caps to set into the socket.
These fuses are available in different current ratings and sizes. In automobile applications, these fuses are used as backup protection for motors, wiring, and short circuits.
Blade-type fuse has a low cutoff current.
Advantages Of HRC Fuse
HRC fuse has the following advantages:
- Fast operation
- Has the capacity to clear the high-fault current
- Not deterioration for a long period
- No maintenance
- Reliable operation
- Consistence performance
- HRC fuse is cheaper compared to other circuit breakers
Disadvantages
high rupturing capacity fuse has the following Disadvantages:
- It required replacement after each operation
- Interlocking is not possible
Application HRC Fuse
Applications of High rupturing capacity fuse as given below
- Protection of low voltage distribution system
- Protection of motor
- Protection of bus bar
- Protection of semiconductor devices
- Use as backup protection to the circuit breaker.
